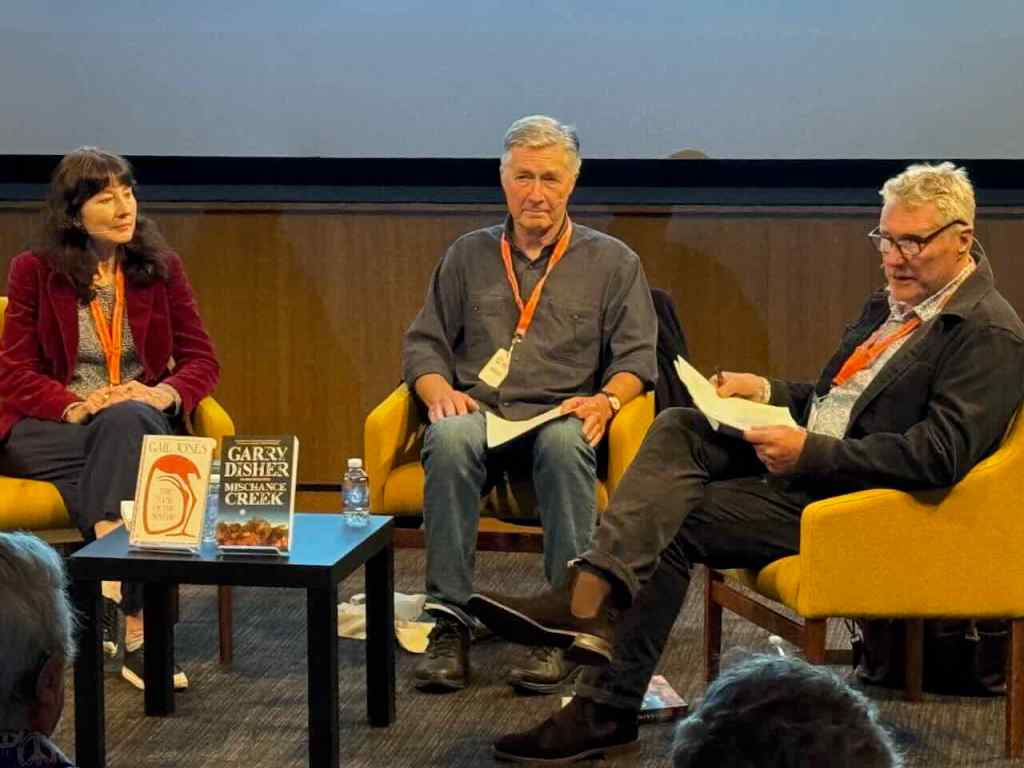
Garry Disher and Gail Jones with Michael Brissenden
The program described the session as follows:
Join two of Australia’s most highly regarded writers speak about the lure of the Australian outback with its landscapes, characters and unsettled complexity. Here we have different tales of desperate searches to uncover what has happened to two women in the outback. Stories multiply. Heart and horror beat in tandem. Cops try to do their best. Gail Jones (The Name of the Sister) and Garry Disher (Mischance Creek: The new Hirsch novel) will together explore the power of beautifully written outback crime. Moderated by Michael Brissenden (Dust)
Journalist and novelist Michael introduced the authors, outlining their work and achievements before getting onto the discussion which centred, of course, around two concepts – the outback and writing about crime. It was an intriguing if sometimes slightly odd discussion, with Gail Jones talking almost as much about Disher’s work as her own, and an underlying (but also explicitly explored) tension between literary writing and crime (or genre) writing.
The session started with the usual question asking the writers to précis their novels. Gail Jones described hers as non-genre, and said it was set in Sydney, Broken Hill and Berlin. It starts not with a death of a woman but with a woman being found. It doesn’t have a traditional crime plot, and is about people whose stories and identities are lost.
Garry Disher’s book, on the other hand, does have a crime plot. It’s the 5th in his Hirsch series, but Hirsch doesn’t match the common tropes of crime. Most crime fiction, for example, is closely related to place – think Bosch in LA and Rebus in Edinburgh, for example. Hirsch, however, is from Adelaide, and is an outsider in the small town he has retreated to (though of course, the novels are imbued with this new-to-him place). Most crime fiction protagonists are relatively senior in rank, but Hirsch is lowly. And finally, most crime protagonists are troubled, dark, while Hirsch is genial. The driver for the novel, Garry said – though it was written before the 2025 Porepunkah incident – was the idea of sovereign citizens and their capacity for violence, but there is another plot involving a woman who has come to town, unhappy with the investigation into a case concerning her parents.
The discussion proper then started with that question that won’t go away concerning whether a distinction still exists between literary and crime fiction. Gail said “good writing is good writing”, and that the concept of “literary” is less a judgement of writing than about subject and mode. She is interested in writers who “don’t stay in their lane”. She has also been interested in crime and guilt for a long time, but is less interested in plot than in exploring consciousness, and the covering over or hiding of crime, and secret guilt. When it was suggested to her that she write a crime story, she thought about loss and the dissolution of marriage (which she admitted is probably a more common “literary fiction” subject). Her novel intersects between crime and literary.
Garry addressed Brissenden’s question concerning how crime fiction is changing and where it is now. He delved back into the past, and how in planning for the Spoleto Festival (which has now morphed into the Melbourne Writers Festival) he had suggested inviting Peter Corris, the popular and successful Sydney crime writer at the time, but was firmly told “no, this is a literary festival”. There is still a sense of this divide. He would like to talk about fiction more broadly but he is always invited onto crime panels at festivals – organisers, take note! He senses that there’s a feeling crime writers would embarrass other writers if they appeared together (though didn’t explain what he meant by “embarrass”). His early writing was not crime, and writing craft is important to him. What matters most to him is the characters not the plot.
The conversation then got onto the outback, the session’s subject. Garry said that the term “outback noir” was coined by a journalist talking about the early work of Jane Harper and Chris Hammer, but feels that it has had its day. Writers jumped on the bandwagon, resulting in some copycat (my word) novels that were not necessarily good. Good crime, all agreed, deals with prevailing social values and conditions – well-written and in an entertaining way, said Brissenden.
So, what is this thing called the outback, and to what degree does it play into the concept of place and character? This is where the session became particularly interesting to me, because we bandy around this term, often without a great deal of thought.
Gail thinks it is an antiquated term that she believes began with Lawson’s 1893 poem “Out back”, which has words like “blistering”, “furnace”, and concludes with “Where the bleaching bones of a white man lie by his mouldering swag Out Back”. The poem implies “out back” is homicidal to white men, and “extinguishes”, said Gail, First Nations people. It flattens and reduces the land to one idea, one, more often than not, reduced to a sort of psychodrama. It’s interesting that we (as in non-Indigenous Australians) use “outback” rather than “country”. Our usage – incorporating a sense of being in “the middle of nowhere” – denies the fact that it is other people’s “somewhere”.
Garry agreed with Gail, building on it and adding his own thoughts. Most of us, he suggested, have a vision of the “outback” as vast and encompassing long drives, but also with a mythical overlay, as reflected in “we of the never never” (Mrs Aeneas Gunn) and “the great Australian loneliness” (Ernestine Hill). The sense – also conveyed in paintings by artists like Russell Drysdale and Sidney Nolan – is that it is remote, not pleasant, even though it is home to someone. The outback (like the beach) suggests loss – lost children, lost travellers, the lost women in their novels. On the other hand, there’s the “outback” that is romanticised by travel companies.
Gail added that the challenge is learning about the Indigenous world view, their knowledge of and regard for land. White Australia has not come to terms with the mysticism and animism associated with First Nations’ understanding of the land, a place rich with meaning. The travel idea of “adventure” misrepresents what the land is, but has extraordinary persistence. Similarly, she said, the ideas of “noir” and “gothic” (which originated in 18th century England and Walpole’s Castle of Otranto) come from other lands and cultures, and are a mismatch with the outback. She likes that Garry’s Hirsch is richly human and that his novels include women and Indigenous people.
We then moved onto the idea of loneliness in a sparse place. Garry reiterated that Hirsch is an outsider, without deep friendships (though he has a lover living outside the town). He has to be all things to all people. Gail’s character Angie is a freelancer which can be a lonely occupation, but Gail is more interested in solitariness rather than loneliness.
Gail didn’t want to have cop character in her novel because she doesn’t know police stations and procedures, but she had to “get out of Sydney”. She is interested in mining towns – her father was a miner, one of the “labouring poor” – so she could relate to the harshness of Broken Hill. She commented on the profound masculine overlay there created by films/novels like Wake in fright and the Mad Max movies, while Hirsch, she said, despite being a male cop in a small town, is aware there are other meanings – layers – in the place. She likes crime that has this social complexity.
Talking fathers, Garry said his told him that farming was a mug’s game and to get an education, which he did. This included researching the landscape writers of the 1930s with their complicated messages about the outback (including towards Indigenous people who were either feared or treated as children). However, his brother became a small town cop. He can go to him for practical questions (like would a paddy wagon be air-conditioned?)
There was more, including readings by both from their novels, and a comment from Gail about liking it when policemen/detectives in crime novels are also readers! Hirsch for example mentions Helen Garner’s diaries.
Oh, and for those interested, there will be another Hirsch novel, but he does write standalone novels in between. The next one draws on children’s fears (like his in the 1960s about Russians and communists.)
There was no Q&A. And we didn’t really need it after this thoughtful, deep dive into “the outback”.
Canberra Writers Festival, 2025
What happened in the outback
Saturday 25 October 2025, 10-11am